The deforming arthrosis of the knee joint is called gonartrosis in medicine-this is a degenerative-dystrophic disease in the hyalin cartilage of the knee, which covers the condyles of the femoral and tibia.
With arthrosis of the knee joint, the symptoms develop gradually, for years, the main manifestation of the disease is pain, stiffness during movement. It is gonarthrosis that is considered the most common disease among arthrosis of other joints, such as hip arthrosis, arthrosis of the elbow or shoulder joints, and phalanges of the fingers.
Most often, the disease affects faces over 40, women are most susceptible to arthrosis. Sometimes it develops in young people against the background of injury or in athletes from excessive loads.
Knee arthrosis: symptoms, causes, stages of the disease
Symptoms of knee arthrosis.
There can be several symptoms of a serious disease (arthritis of bones, joints), and not all occur at once, but gradually as cartilaginous tissues are destroyed.
Consider the symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint at all stages (stages) of the disease.
At the initial stage, the patient has a minimum of discomfort, but even a slight, but quite sharp pain in the knee joint begins to appear. A problem becoming a trip or long hiking becomes problematic. Further, the pain that endured the body begins to aggravate and the person already becomes uncomfortable in the knees, after some physical exertion or when rising from sedentary positions, when there is a load on the lower part of the limbs. In such cases, they feel a sharp pain in cartilage or in the very joint of the knee. Such pain quickly leaves, but each time it returns.
At the next stage of the disease, not only painful sensations are enhanced, but also begins to modify the knee. Due to the fluid accumulated in the cartilaginous tissue, the knees can become spherical and slightly swell.
Further, everything is worse. If the disease is not treated, the process of blood circulation is disturbed in the knee, the hyalin cartilage area dry out, and the cartilage itself can crack, after which it will begin to collapse, and various kinds of growths will begin to appear on the bone structure. At this stage, the movement of cartilage is already very difficult, and every step is given to a person with difficulty. Walking causes severe pain, which practically does not end, and discomfort, cartilage degeneration occurs.
The last stage of the disease is when the knee joint is already completely affected, there is no cartilage fabric in the knee, and a person without support simply cannot sit down and stand up, cannot fully move, without experiencing severe pain in his such movements.
- Symptoms that need to be reacted to. A person must react even when the pain that occurs in the knee begins at the slightest stresses and stresses on the leg, when when walking or squats, a crunch of knees occurs, when movements are discomed to it, his legs get tired quickly, swelling appears in the knees.
- What to do if the joints hurt? If the joints of the knees began to hurt or there was a sharp pain in the cups when you get up and sit down, consult a doctor immediately. Do not wait until the arthrosis of the knee joint will hit the joint and the cartilage of the knee completely, go to the doctor as soon as you felt the very first symptoms of the disease. Remember, when the disease already completely impressed the cartilage tissue, the deformation of the bone occurs and the pain does not subside either day, nor at night, nor when walking, or without it.
- When to contact a rheumatologist? A person should be addressed to a rheumatologist at the first manifestations (symptoms) of the disease.
- The main symptoms of arthrosis. The main symptoms of knee arthrosis, on which you should build your attention: the pains of any intensity and strength in the knees or one knee, which are felt by a person when lifting from a position sitting or lying, when walking; the pain that manifests itself in the knee cups during lifts on the stairs; The occurrence of pain syndrome immediately after a person comes out of a state of rest, for example, rises after sitting and begins to move.
The causes of arthrosis of the knee joint.
The arthrosis of the knee joint can hit a person for a number of reasons - this is age (over the years the cartilage wears out), and intense physical therapy on the leg or leg, and various kinds of knee injuries, and much more.
The main reasons for the development of arthrosis:
- Overweight.
- Elderly age.
- Heredity.
- Osteoporosis.
- The deficiency in the body of vitamins and useful trace elements necessary for bones.
- Specific work with constant loads on the cups of the knees.
- Metabolic disorders.
- Sports (intensive training, load on one leg or both legs).
- Knee injuries.
To avoid disability, you should consult a rheumatologist in time for a qualified assistance.
What happens to the joint with arthrosis.
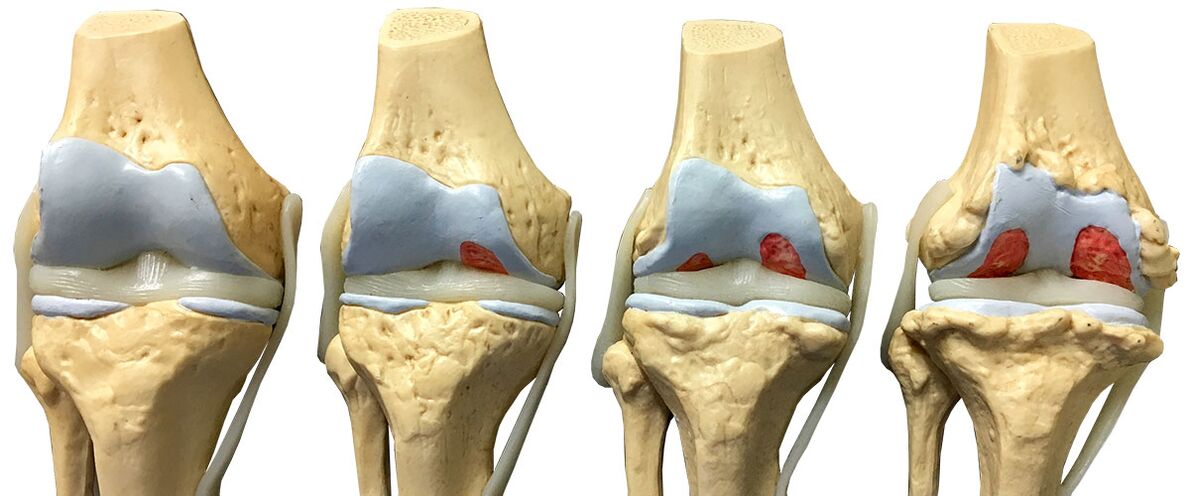
At each stages of the disease, its modifications occur in cartilage, in the joints and bones of the knees.
So, at the very beginning of the development of the disease, the cartilage softens hard, become very vulnerable. Further, microcracks and small tears, which gradually increase, appear on the surface of the joints. The next stage - cartilage begins to grow and increase in thickness. The last stage is the complete destruction of the cartilage on a specific or some particular section of the joint.
Arthrosis of the knee joint, degree of disease
All rheumatologists reveal the three degrees of arthrosis of the human knee.
First. It is characterized by a slight narrowing of the slots directly between the joints themselves, which leads to slight discomfort and no constraint of movements.
The second. On it, doctors note a pronounced narrowing of the cracks between the joints, the formation of osteophytes and cysts, the appearance of a strong crunch in the knees.
The third and last. On it there is a change in the forms of osteophytes, a partial or complete change (destruction) of the bones occurs, the movement of the legs in the knees becomes impossible.
The degree of arthrosis of the knee joint
- Arthrosis of the knee joint 1 degree. At this stage, the ailment is only emerging, the cartilage is almost whole and the bones are not deformed. At this time, people feel infrequent pain in the knee cups with some, even frivolous loads on their leg. These pains pass, but then they arise again and again, pass and appear again, already become more frequent, swelling may begin, which, according to the observation of patients, takes place without taking any pills and the use of ointments.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint 2 degrees. This stage is already characterized by slightly large pains in comparison with the initial stage. The pain occurs not only if there is an intensive load, but also with ordinary walking, when lifting severity, when rising from a sitting position. A distinct crunch of knees begins to hear. Already at the indicated stage begins gradually, slowly or intensively (depending on the individuality of the body), the joint is deformed, human movements become limited.
- Arthrosis of the knee joint 3 degrees. At the last, and this is the third, the degree of our disease, the symptoms are already very expressed very much, the pain in the joints of the knees are regular, and the modification of the bones is already noticeable by the eye. Human mobility is almost completely limited, it is very difficult for the patient to choose a convenient position for himself, the pain does not subside.
Arthrosis of the knee joint - symptoms and treatment
General symptoms include:
- the feeling of pain in the cups of the knees when a person moves (the onset of the disease);
- pain in the affected areas, which every day becomes stronger;
- night pain in the joints of the knee;
- edema in areas affected by the disease;
- Rough dry crunch of knees;
- Deformation of bones in places affected by the disease.
The main symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint
The main (the main, according to doctors-russia) symptoms of arthrosis are four.
These include:
- pain during the movement of the knees;
- dry crunch in affected places;
- reduction in the ability to move sick legs;
- Changes external (full or partial) affected areas.
- Diagnosis and treatment for arthrosis of the knee joint.
Having carefully examined the patient, the rheumatologist assesses the situation, turning his gaze to the changes visible by the eye in the areas of one knee or both and their direct mobility. The probing method sets the places of pain and crunch, as well as the intensity of these pains.
In addition to an X -ray for the patient, the doctor prescribes computed tomography and (or) MRI. These studies are necessary to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct treatment.
Treatment of knee arthrosis, treatment methods
Treatment of arthrosis of any stage of the knee joint includes:
- treatment methods using medicines;
- treatment methods using exercise therapy and special physiotherapy;
- treatment methods using the most ordinary massage;
- Surgical intervention.
What gives effective therapy.
Effective therapy prescribed by a doctor contributes to:
- removal of sharp pain;
- the restoration of the destroyed cartilaginous tissue (if possible, the outcome depends on the degree of illness);
- increased joint mobility.
In the elimination of knee arthrosis, exercise therapy plays a special role, a special diet based on legumes and dairy products and massage. If the prescribed therapy for one reason or another did not show the desired result, the patient is prescribed an operation to install a special prosthesis replacing the joint.
Arthrosis of the knee joint: treatment, drugs
A competent treatment with arthrosis of the cartilaginous tissues of the knee joint (violations of the cartilage composition) prescribed by the rheumatologist includes a whole complex of drugs. This treatment complex usually includes:
- Nesteroid, aimed at removing inflammation, drugs.
- Chondroprotectors.
- Special creams or ointments.
- Therapeutic agents on the basis of which compresses are made.
Most often, for the treatment of arthrosis of the knee cartilage, doctors prescribe ibuprofen of any manufacturer, indomethacin also of any production, ketoprofen, diclofenac, pyroxics and others.
The appointment of these drugs contributes to the rapid elimination of pain, as a result of which the patient can begin fruitful treatment in other ways - the method of massage, medical exercises, etc.
As for ointments, most often for the patient the use (rubbing with massage movements into the sore area) of such drugs in the form of dense ointments (creams) and gels, such as diclofenac, Fastum, Ferbedon, Transivazin, Dolgit and others.
The list of special gels and ointments - external preparations for joints in the modern pharmacological market is very wide and diverse, and therefore, on the recommendation of a doctor, the patient can choose from the total number the most suitable and effective specifically in his case.
Some of the most popular recipes for traditional medicine against knee arthrosis.
- Treatment with a burdock or the most ordinary burdock. For treatment, it is necessary to (it is necessary to take three sheets of burdock (it is better to take young leaves), attach them to the sore knee and wrap them with gauze, which is sold in any pharmacy, or bandage. On top of Marley, it is also best to use a warm down scarf. The procedure should be repeated daily before bedtime, leaving burdock leaves in a sore spot for the whole night.
- With arthrosis and juice of the plant, celandine will help. You need to buy or get celandine juice yourself. Having saturated with such juice a linen or any other natural fabric, apply it to a sore spot for 45-55 minutes. Having removed the bandage, immediately grease the joint with any vegetable oil. Repeat the treatment for at least 10 days, then take the same break and repeat the course again.
- Treatment of arthrosis by a dandelion. For such therapy, it will be necessary to make a collection of flowers of a blossoming dandelion. To obtain the proper effect, folk healers recommend that patients daily eat five dandelion flowers on an empty stomach, previously lowered into boiled warm water and washed in it. In addition, from dandelion flowers, you can make a special grinding infusion. To do this, a bank is taken, which is previously treated with boiling water, half filled with dandelion flowers, and poured (second half of the jar) by conventional by any triple cologne. The product is placed in a dark place and closes under the lid. After 30 days, the infusion can be used for rubbing sore spots. Rubbing movements are performed clockwise for 20-30 seconds per knee.
After using these compresses, about 75% of patients note a significant improvement in their condition, a decrease in pain and almost complete disappearance of a characteristic crust of the knees.
ShouldRemember that recipes for traditional medicine do not treat the disease, they can only supplement the therapeutic course of treatment with medicines, making this course more effective.
If you prepare any of the means of traditional medicine or correctly prepare raw materials for such a tool, you are not able to independently, it is better to purchase such components in a pharmacy or ask to collect plants of knowledgeable people (folk healers, grandmothers).
Therapeutic gymnastics
A special place in the treatment of arthrosis in the knees is occupied by special therapeutic gymnastics (exercise therapy). It is prescribed to patients, regardless of the treatment process in order to improve the flow and outflow of blood in a affected area, increase muscle strength and prevent contractures. Shown together with the use of special drugs.
LFK for arthrosis is by no means a specific treatment, it is an auxiliary method of combating the disease that is prescribed in combination with a course of special medicines.
Several exercises of therapeutic gymnastics for treatment and prevention:
- It is necessary to go to a hard place (floor). Bend and immediately extend the knees at once with both legs. It is recommended to repeat the exercises for 3-5 minutes as often as possible in a day. The load on both legs should be the same.
- Lying on the back, on the floor, cross your legs with scissors (foot on the leg, first the right leg from above, then from below), holding your knees in an exposed state. Such movements are recommended to be repeated every day. Exercises should not cause discomfort, with pain it is better to abandon such an exercise.
- Lying on your back, in a solid place, pushing it in turn to your stomach, bending one other leg in the knee. These movements, performed daily, will help exclude you from the risk zone. The exercises are recommended to repeat every day for 3-4 minutes as often as possible. The load on both legs, as in the first case, should be the same.
An exercise therapy for the treatment of arthrosis of the articular knee cartilage will bring more benefits if you combine therapeutic exercises with a special massage.
Visible changes in the condition with the use of physiotherapy exercises in the patient can occur in 7-10 days.
If you are not able to perform exercise therapy yourself, it is better to refuse exercises.
Arthrosis of the knee joint: the first symptoms, treatment, prevention and diet
Summing up, they would like to notice that having discovered the first symptoms of the disease, and these are pain in the knee joints and a characteristic crunch, immediately go to the doctor and start special treatment with medications.
A diet that will help with arthrosis.
Immediately if you find arthrosis or in order to prevent the disease, review the diet of your usual diet. In the daily diet, there should be a steamed dish or boiled. It is best if foods that have a beneficial effect on bones, ligaments, joints, and cartilage are used in food. Such products include: all legumes, cottage cheese, hard varieties of cheese, soup, baked fish, baked fish, hazelnuts, almonds, pumpkin, zucchini, carrots, broccoli and cauliflower, prepared on the basis of bones.
A diet that is described above is not a specific method of treatment, for effective treatment it should be used in combination with medicines, medical exercises and massage.
The first group of reasons: hereditary and age factors
Heredity
Arthrosis of the knee joint is a disease in which a hereditary predisposition to it is quite pronounced. So, if you are a woman, and your mother suffered from osteoarthritis in any form (not at all-knees), then the probability of getting this disease is 2-3 times higher than on average in the population. If you have sisters and they are also sick with arthrosis, then the probability of its appearance is even more.
In addition, there are diseases with a hereditary predisposition in which the connective tissue is affected - the so -called collagenoses, which include, for example, a sticler syndrome. In the presence of such defects on the part of collagen - a substance that is part of the ligaments - the probability of developing the disease also increases.
Partly to this group of causes of arthrosis of the knee, diseases of the endocrine system are adjacent: diabetes mellitus, lack of female sex hormones in menopause and a number of other conditions.
Age
Unfortunately, the older the person becomes, the higher he has the risk of osteoarthrosis. This is due to the fact that with age the ability of cartilage to regeneration and restoration falls, and the metabolism in the joints deteriorates.
So, if at the age of 45, this ailment suffers from 1. 5 to 3-4% of the population (US data), then almost every third person is sick in the interval of 45 to 65 years (30%). And at the age of 65 to 85 years, the frequency of development of the disease jumps up to 80 or more percent!
In addition, in patients of mature age, the development of the disease is influenced not only by age in itself, but also by hormonal changes. So, in women in menopause, the probability of the development of osteoarthritis increases sharply. This is due to the fact that estrogens - female sex hormones - regulate the processes of metabolism in the joints, cartilage, bones and ligaments. When they become smaller (when menopause), the metabolism in these tissues worsens and the risk of osteoarthrosis increases sharply.
Second group of causes: congenital and acquired diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Inflammation of the joint
Inflammation of the knee joint (arthritis, more precisely, drives) is one of the most common causes of gonarthrosis. Unfortunately, most of the microorganisms that penetrate the joint and cause its inflammation contribute to the fact that the delicate cartilage is deformed. At the same time, its nutrition worsens significantly, the shape of the cartilaginous surfaces of the bones changes, etc.
Due to all these reasons, the normal sliding of the cartilage in the articular bones is disturbed. This leads to additional trauma of the cartilage, worsens the volume of movements in the joint and, to the end, creates a very fertile ground for the development of osteoarthrosis.
Operations and injuries of the knee
Another common cause of the disease is the presence of knee injuries and surgical interventions on it. Very often there is both one and the other - for example, when, as a result of sports injury, an operational removal of meniscus is carried out. The normal function of the joint is impaired, the load on the cartilage changes, intensifying in atypical places, and as a result, the osteoarthrosis of the knee is formed.
Metabolic disorder in the body
The cartilage fabric in the joints is one of the few, the nutrition of which does not occur through the delivery of nutrients through blood vessels. The cartilage is "eaten" by diffusion of nutrients from synovial fluid, as well as directly from the pineal glands according to the same principle.
This is a rather subtle and fragile mechanism, therefore, if various metabolic disorders occur in the body, it can break and stop working. Therefore, some diseases in which the metabolism in the body is greatly disturbed can contribute to osteoarthrosis.
Such diseases include primary and secondary gout, joint chondromatosis, hemochromatosis, ocronosis, as well as Wilson-Konovalov’s disease and a number of other diseases. In addition, endocrine diseases can also be added to this group that also affects the metabolism in the entire body - diabetes mellitus and a lack of female sex hormones (estrogen) in old age due to menopause.
Third group of reasons: increased loads and microtrauma cartilage
Sports and hard physical work at work
As already mentioned, the nutrition of cartilage is a very subtle mechanism that can disrupt not only metabolism problems, but also increased loads on the knee joint.
This happens quite often with intensive sports, as well as when a person’s work involves high physical activity, as well as prolonged standing on his feet without the ability to sit down and relax.
At the same time, certain muscle groups (for example, the muscles of the lower leg and thigh) are overstrain. This worsens nutrition in the muscles and joints, which means that there are problems with the metabolism inside the cartilage, when cartilages simply do not have time to recover after such strong physical exertion on the joint.
Diagnosis of arthrosis
Arthrosis of the knee joint should be differentiated (distinguished) from rheumatic, inflammatory and some other diseases with similar symptoms.
For this, a standard examination standard has been adopted, which includes a general biochemical blood test, radiographic examination, MRI and ultrasound.
With arthrosis, a blood test does not reveal significant deviations from the norm. A change in the composition of the blood, an increase in the level of immune cells and antibodies usually indicates another disease.
Since arthrosis does not manifest in analyzes in any way, the only reliable way to diagnose it is a hardware examination.
X -ray, as the most common and cheapest method of examination, is able to relatively accurately identify arthrosis and its stage.
In the picture, structural changes in the joints and bones are clearly distinguished. X -ray examination makes it possible to detect structural deformations, determine defects in the articular surfaces.
For a reliable determination of gonarthrosis and the stage of its development, an additional examination is used in conjunction with x -ray: on ultrasound, MRI or CT apparatus.
The methodology for the diagnosis of arthrosis is designed to ensure accurate detection of the disease at the earliest stages of development, which will effectively treat it.
Unfortunately, due to the specifics of the disease, the effectiveness of this approach is small: patients are inclined not to pay attention to weak pain and slight chroma, and are led to the doctor already at the second or third stage of gonarthrosis.
Additional recommendations: Prevention
Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating risk factors that lead to the development of arthrosis.
It is recommended to engage in moderate physical activity. In this case, the possible injury, overvoltage and hypothermia of the joints should be avoided.
As noted above, no connection between the diet and the risk of developing arthrosis has been established.
However, it is recommended to reduce the consumption of salted and spicy foods, alcohol and cigarettes: this will improve the general condition of the body and reduce the load on the joint.
In the presence of a family history, indicating a genetic predisposition, a physical examination should be regularly underwent. In general, the prevention of arthrosis is to lead a moderate lifestyle. It is important not to start the disease and consult a doctor at the slightest suspicion of arthrosis.